/ home / newsletters /
Bitcoin Optech Newsletter #181
This week’s newsletter describes an alternative proposal to slowly phase
in full replace-by-fee and announces a series of meetings to review the
proposed OP_CHECKTEMPLATEVERIFY soft fork. Also included are our
regular sections with announcements of releases and release candidates
and summaries of notable changes to popular Bitcoin infrastructure
projects.
News
-
● Brief full RBF, then opt-in RBF: Jeremy Rubin replied to an older Bitcoin-Dev mailing list thread described in Newsletter #154 about enabling full replace by fee (RBF) in Bitcoin Core. Currently, any transaction that signals according to BIP125 can be replaced by a higher-feerate alternative (with some restrictions). The previous proposal was to eventually allow any transaction to be replaced (“full RBF”)—not just those that set the opt-in signal that replaceability is wanted. Some merchants have indicated that they prefer that relay nodes make replaceability as hard as reasonably possible, at least optionally, so that they can immediately accept unconfirmed transactions in exchange for low-cost goods and services.
Rubin’s alternative still encourages moving to full RBF, but suggests starting by allowing full RBF of any transaction for n seconds after it is first received by a node. After n seconds, the BIP125 opt-in flag is honored the same as now. This can allow merchants to accept unconfirmed transactions like they do now after those n seconds have elapsed. More importantly, it may allow protocols that depend on replaceability for security to not have to worry about non-opt-in transactions as long as a protocol node or watchtower can reasonably respond within a fraction of n seconds of first learning of a transaction.
-
● BIP119 CTV review workshops: Jeremy Rubin announced on the Bitcoin-Dev mailing list that he will be hosting recurring meetings to discuss BIP119’s specification of OP_CHECKTEMPLATEVERIFY, including how it could be deployed on the network. The first meeting will be held Tuesday, January 11th, at 20:00 UTC in ##ctv-bip-review on Libera.Chat. Subsequent meetings will be held at the same time every two weeks indefinitely.
Releases and release candidates
New releases and release candidates for popular Bitcoin infrastructure projects. Please consider upgrading to new releases or helping to test release candidates.
- ● Rust-Lightning 0.0.104 is the latest release of this LN node library containing several API improvements.
Notable code and documentation changes
Notable changes this week in Bitcoin Core, C-Lightning, Eclair, LND, Rust-Lightning, libsecp256k1, Hardware Wallet Interface (HWI), Rust Bitcoin, BTCPay Server, BDK, Bitcoin Improvement Proposals (BIPs), and Lightning BOLTs.
-
● Bitcoin Core #23789 causes newly created change outputs to always match a destination’s output type, while still preferring to create P2TR change outputs when possible. This PR addresses a privacy concern that early taproot adopters’ change outputs can be easily identified when they pay legacy addresses.
-
● Bitcoin Core #23711 documents several aspects of Bitcoin Core’s policy for accepting and relaying unconfirmed transactions. The documentation may be especially useful for authors of wallets and contract protocols who need to depend on acceptance and relay behavior.
-
● Bitcoin Core #17631 adds a new REST endpoint that provides compact block filters on nodes that have filters and REST endpoints enabled.
-
● Bitcoin Core #22674 adds the logic for validating a package of transactions and testing it against the node’s transaction relay policy. A package in this case is one child transaction and all of its unconfirmed parents. Follow-up PRs are expected to extend the validation logic by adding support for CPFP and RBF.
In a later follow-up PR, a method may be added to allow peers to submit packages of transactions to the local node which will be validated using the now-available logic. That will enable package relay, enhancing the reliability and security of contract protocols such as LN. The PR also adds documentation about the package validation rules.
-
● Bitcoin Core #23718 adds support for retaining and displaying any hashes and preimages contained in a PSBT. PSBTs used for HTLCs or other contract protocol primitives may contain a hash whose preimage is known by one of the PSBT updaters or signers. That preimage may need to be provided in order to generate the desired final transaction. This PR brings Bitcoin Core closer to being able to effectively participate in the creation, management, and finalization of such transactions. Additional improvements are expected if Bitcoin Core adopts support for miniscript.
-
● Bitcoin Core #17034 adds support for version 2 PSBTs (see Newsletter #128) and additional PSBT fields, including the fields for proprietary PSBT extensions described in Newsletter #72. Bitcoin Core doesn’t understand the proprietary extensions but will now preserve them in PSBTs it processes and display them in the results of the
decodepsbtRPC. -
● Bitcoin Core #23113 updates the
createmultisigandaddmultisigRPCs to include a warning field if the user requests the creation of a segwit multisig address using an uncompressed public key. Since the original implementation of segwit, Bitcoin Core has defaulted to not relaying or mining unconfirmed transactions that spend segwit inputs with uncompressed public keys. That means any user who creates an address using an uncompressed key may not be able to spend any funds received to that address. For that reason, these RPCs never create bech32 addresses for uncompressed keys—they instead create legacy (base58check) addresses. The new warning field should help users in this situation understand why they’re receiving a different address type than what they requested. -
● Bitcoin Core GUI #459 updates the generate-address dialog with the ability to create bech32m addresses in addition to older address types.
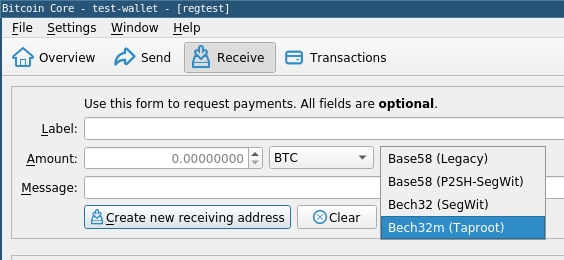
-
● Eclair #2090 adds support for rate limiting onion messages via the
max-per-peer-per-secondconfiguration option. -
● Eclair #2104 adds a log message that warns the local node operator when their immediately onchain spendable balance has dropped below the estimated amount necessary to use CPFP fee bumping with anchor outputs to close their channels in a timely manner. LN developers or operators choosing their own reserve values may wish to compare the estimates Eclair has made to those used in LND.
-
● Eclair #2099 adds an
onion-messagesconfiguration option that can be set to never relay onion messages (but still allow the node to send or receive messages), relay all messages (even those that require opening a connection to a new peer), or only relay messages over existing connections. -
● Libsecp256k1 #964 outlines a release process and a versioning scheme for the libsecp256k1 library.
-
● Rust Bitcoin #681 adds support for BIP371’s additional PSBT fields for taproot.
-
● Rust-Lightning #1177 drops the need for Rust-Lightning itself to store information about payments the higher-level wallet application wants to receive. Instead, the essential information about the payment is encrypted and then encoded into the payment secret. When a payment is received, the encrypted payment secret is decrypted and the plaintext information is used to derive the payment preimage used to satisfy the payment hash used to secure the payment’s HTLC.
This is a simplified implementation of the idea described in Newsletter #168. Other LN implementations may store information about an invoice (e.g. an arbitrary order identifier provided by a merchant’s shopkeeping software), but Rust-Lightning sidesteps that as it is a library that expects to be integrated directly into a higher-level app and so allows the higher-level application to manage the details of its own payment requests.
-
● HWI #545, #546, and #547 add support for taproot by enabling support for
tr()descriptors, BIP371 support for taproot PSBT fields, and support for bech32m addresses for taproot scripts when available in the underlying hardware signing devices. Note, as of these PRs, HWI does not fully support some signing device firmware that does support taproot, so taproot support is not yet enabled on those devices. -
● BIPs #1126 adds BIP52 for Optical Proof of Work (OPoW), a proposed hard fork change to Bitcoin that is claimed will change the division of costs between mining equipment (capital expenditures) and electrical and operation costs (operational expenditures). The idea was previously discussed on the Bitcoin-Dev mailing list, where it had both supporters and detractors.
